Next Previous Up Contents
Next: Label Form
Up: Plot Forms
Previous: Linear Fit Form
The Quantile form ( )
plots a line through a given quantile of the values binned within
each pixel column (or row) of a plot.
The line is optionally smoothed using a configurable kernel and width,
to even out noise from the pixel binning.
Instead of a simple line through a given quantile, it is also
possible to fill the region between two quantiles.
)
plots a line through a given quantile of the values binned within
each pixel column (or row) of a plot.
The line is optionally smoothed using a configurable kernel and width,
to even out noise from the pixel binning.
Instead of a simple line through a given quantile, it is also
possible to fill the region between two quantiles.
One way to use this is to draw a line estimating a function
y=f(x) (or x=g(y)) sampled by a noisy set of data points
in two dimensions.
Note:
In the current implementation, depending on the details of the
configuration and the data, there may be some distortions or missing
graphics near the edges of the plot.
This may be improved in future releases, depending on feedback.
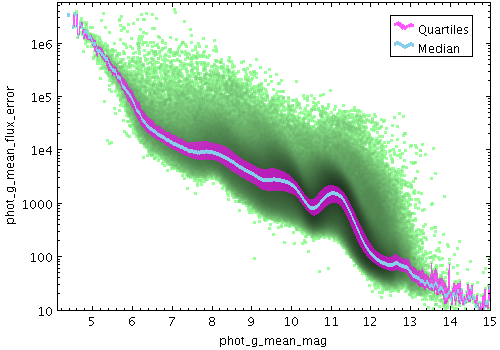
Example Quantile plot
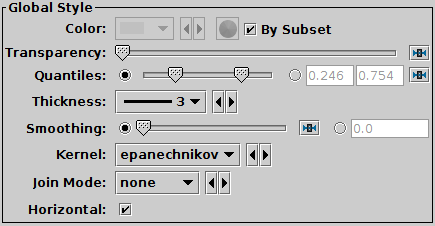
Quantile configuration panel
The configuration options are:
-
Transparency
- Transparency with which components are plotted,
from opaque to invisible.
-
Quantiles
- Defines the quantile or quantile range of values that should be
marked in each pixel column (or row).
The slider control goes from 0 (minimum in pixel column/row)
to 1 (maximum in pixel column/row), so 0.5 indicates the median.
This control is a double-slider, so you can drag out a range
of values. If the values are the same as each other, a single
point will be indicated, but if there is a range then the area
between the indicated quantiles will be filled.
The radio buttons let you toggle between using the slider to
set the quantile value(s) or entering them in the text fields.
If the two values are identical, you can leave the second text field blank.
-
Thickness
- Sets the minimum extent of the markers that are plotted in each
pixel column (or row) to indicate the designated value range. If the
range is zero sized (two bounding quantiles are equal)
this will give the actual thickness of the plotted line.
If the range is non-zero however, the line may be thicker than this in
places according to the quantile positions.
-
Smoothing
- Configures the smoothing width.
This is the characteristic width of the Kernel
function to be convolved with the density in one dimension
to smooth the quantile function.
You can adjust it using the slider (wider smoothing to the right)
or enter a value in data coordinates explicitly in the text field.
If the smoothed axis is logarithmic, the value is a multiplication factor
rather than an additive increment.
-
Kernel
- The functional form of the smoothing kernel. The functions listed
refer to the unscaled shape; all kernels are normalised to give a
total area of unity.
The available options are:
-
square:
Uniform value: f(x)=1, |x|=0..1
-
linear:
Triangle: f(x)=1-|x|, |x|=0..1
-
epanechnikov:
Parabola: f(x)=1-x*x, |x|=0..1
-
cos:
Cosine: f(x)=cos(x*pi/2), |x|=0..1
-
cos2:
Cosine squared: f(x)=cos^2(x*pi/2), |x|=0..1
-
gauss3: Gaussian truncated at 3.0 sigma:
f(x)=exp(-x*x/2), |x|=0..3
-
gauss6: Gaussian truncated at 6.0 sigma:
f(x)=exp(-x*x/2), |x|=0..6
-
Join Mode
- Defines the graphical style for connecting distinct quantile values.
If smoothed samples are packed more closely than the pixel grid
the option chosen here doesn't make much difference,
but if there are gaps in the data along the sampled axis,
it's useful to have a guide to the eye to join one quantile
determination to the next.
The available options are:
-
none:
displayed quantile ranges are not joined
-
polygon:
the area between a line connecting the upper quantiles
and a line connecting the lower quantiles is filled
-
lines:
a line of thickness given by Thickness
is drawn from the center of each quantile range to the next
-
Horizontal
- Determines whether the trace bins are horizontal or vertical.
If true, y quantiles are calculated for each pixel column,
and if false, x quantiles are calculated for each pixel row.
Next Previous Up Contents
Next: Label Form
Up: Plot Forms
Previous: Linear Fit Form
TOPCAT - Tool for OPerations on Catalogues And Tables
Starlink User Note253
TOPCAT web page:
http://www.starlink.ac.uk/topcat/
Author email:
m.b.taylor@bristol.ac.uk
Mailing list:
topcat-user@jiscmail.ac.uk
![]() )
plots a line through a given quantile of the values binned within
each pixel column (or row) of a plot.
The line is optionally smoothed using a configurable kernel and width,
to even out noise from the pixel binning.
Instead of a simple line through a given quantile, it is also
possible to fill the region between two quantiles.
)
plots a line through a given quantile of the values binned within
each pixel column (or row) of a plot.
The line is optionally smoothed using a configurable kernel and width,
to even out noise from the pixel binning.
Instead of a simple line through a given quantile, it is also
possible to fill the region between two quantiles.

