polygon
Draws a closed polygon given an array of coordinates
that define its vertices.
In fact this plot requires the position of the first vertex
supplied as a positional value in the usual way
(e.g. X and Y coordinates)
and the second, third etc vertices supplied as an array
using the otherpoints parameter.
Invocation might therefore look like
"xN=x1 yN=y1 otherpointsN=array(x2,y2, x3,y3, x4,y4)".
Usage Overview:
layerN=polygon useposN=true|false polymodeN=outline|border|fill|cross|star
thickN=<int-value>
shadingN=auto|flat|translucent|transparent|density|aux|weighted|paux|pweighted <shade-paramsN>
<pos-coord-paramsN> otherpointsN=<array-expr> inN=<table>
ifmtN=<in-format> istreamN=true|false icmdN=<cmds>
All the parameters listed here
affect only the relevant layer,
identified by the suffix
N.
<pos-coord-paramsN>
give a position for each row of the input table.
Their form depends on the plot geometry,
i.e. which plotting command is used.
For a plane plot (plot2plane)
the parameters would be
xN and yN.
The coordinate parameter values are in all cases strings
interpreted as numeric expressions based on column names.
These can be column names, fixed values or algebraic
expressions as described in Section 10.
Example:

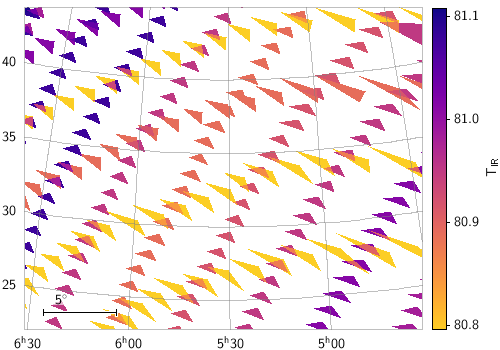
stilts plot2sky in=big_tab_VIR_VIS_CSA_public.fits
icmd='select ALTITUDE>4e4&&ALTITUDE<4.3e4'
layer=polygon polymode=fill
lon=LON_CENTER lat=LAT_CENTER
otherpoints=array(lon_corner_1,lat_corner_1,lon_corner_2,lat_corner_2)
shading=weighted weight=IR_TEMPERATURE auxmap=plasma
texttype=latex fontsize=14 auxlabel=T_{IR}
clon=83 clat=34 radius=11
icmdN = <cmds> (ProcessingStep[])
inN.
The value of this parameter is one or more of the filter
commands described in Section 6.1.
If more than one is given, they must be separated by
semicolon characters (";").
This parameter can be repeated multiple times on the same
command line to build up a list of processing steps.
The sequence of commands given in this way
defines the processing pipeline which is performed on the table.
Commands may alternatively be supplied in an external file,
by using the indirection character '@'.
Thus a value of "@filename"
causes the file filename to be read for a list
of filter commands to execute. The commands in the file
may be separated by newline characters and/or semicolons,
and lines which are blank or which start with a
'#' character are ignored.
A backslash character '\' at the end of a line
joins it with the following line.
ifmtN = <in-format> (String)
inN.
The known formats are listed in Section 5.1.1.
This flag can be used if you know what format your
table is in.
If it has the special value
(auto) (the default),
then an attempt will be
made to detect the format of the table automatically.
This cannot always be done correctly however, in which case
the program will exit with an error explaining which
formats were attempted.
This parameter is ignored for scheme-specified tables.
[Default: (auto)]
inN = <table> (StarTable)
-",
meaning standard input.
In this case the input format must be given explicitly
using the ifmtN
parameter.
Note that not all formats can be streamed in this way.:<scheme-name>:<scheme-args>.<" character at the start,
or a "|" character at the end
("<syscmd" or
"syscmd|").
This executes the given pipeline and reads from its
standard output.
This will probably only work on unix-like systems.istreamN = true|false (Boolean)
inN parameter
will be read as a stream.
It is necessary to give the
ifmtN parameter
in this case.
Depending on the required operations and processing mode,
this may cause the read to fail (sometimes it is necessary
to read the table more than once).
It is not normally necessary to set this flag;
in most cases the data will be streamed automatically
if that is the best thing to do.
However it can sometimes result in less resource usage when
processing large files in certain formats (such as VOTable).
This parameter is ignored for scheme-specified tables.
[Default: false]
otherpointsN = <array-expr> (String)
usepos
parameter.
Some expression language functions that can be useful
when specifying this parameter are
array() and parseDoubles().
The value is an array-valued algebraic expression based on column names as described in Section 10. Some of the functions in the Arrays class may be useful here.
polymodeN = outline|border|fill|cross|star (PolygonShape)
The available options are:
outline: draws a line round the outside of the polygonborder: draws a line butting up to the outside of the polygon; may look better for adjacent shapes, but more expensive to drawfill: fills the interior of the polygoncross: draws a line round the outside of the polygon and lines between all the verticesstar: draws a line round the outside of the polygon and lines from the nominal center to each vertex[Default: outline]
shadingN = auto|flat|translucent|transparent|density|aux|weighted|paux|pweighted <shade-paramsN> (ShapeMode)
[Default: auto]
thickN = <int-value> (Integer)
[Default: 0]
useposN = true|false (Boolean)
[Default: true]